글을 작성하게 된 계기
사람들과 스프링 서버를 만들어보는 프로젝트를 진행하며 컨트롤러가 호출되기 까지의 과정이 궁금해졌고, 학습 과정에서 알게 된 내용을 정리하기 위해 글을 작성하게 되었습니다.
1. DispatcherServlet 초기화
브라우저에 http://localhost:8090/hello를 입력해서 DispatcherServlet이 동작하는 과정을 살펴보겠습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
@ResponseBody
@ResponseStatus(code = HttpStatus.OK)
public String hello() {
return "hello";
}
}
당시 80 포트를 사용하고 있어 90 포트를 사용했습니다. 🐳🐳🐳
1-1. onRefresh, initStrategies
최초로 사용자의 요청이 들어오면 스프링은 DispatcherServlet을 초기화하기 위해 onRefresh 메서드를 호출합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
......
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
......
}
onRefresh 메서드 내부에서는 initStrategies 메서드가 호출되며 차례대로 initMultipartResolver, initLocaleResolver, initThemeResolver, initHandlerMappings, initHandlerAdapters, initHandlerExceptionResolvers, initRequestToViewNameTranslator, initViewResolvers, initFlashMapManager 메서드를 호출합니다. 이 메서드들이 호출되며 DispatcherServlet의 필드들을 초기화합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
......
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
......
private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerMappings = null;
if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) {
Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);
}
}
else {
try {
HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
}
}
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No HandlerMappings declared for servlet '" + getServletName() +
"': using default strategies from DispatcherServlet.properties");
}
}
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
if (mapping.usesPathPatterns()) {
this.parseRequestPath = true;
break;
}
}
}
private void initHandlerAdapters(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerAdapters = null;
if (this.detectAllHandlerAdapters) {
Map<String, HandlerAdapter> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerAdapter.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerAdapters = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerAdapters);
}
}
else {
try {
HandlerAdapter ha = context.getBean(HANDLER_ADAPTER_BEAN_NAME, HandlerAdapter.class);
this.handlerAdapters = Collections.singletonList(ha);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
}
}
if (this.handlerAdapters == null) {
this.handlerAdapters = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerAdapter.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No HandlerAdapters declared for servlet '" + getServletName() +
"': using default strategies from DispatcherServlet.properties");
}
}
}
......
}
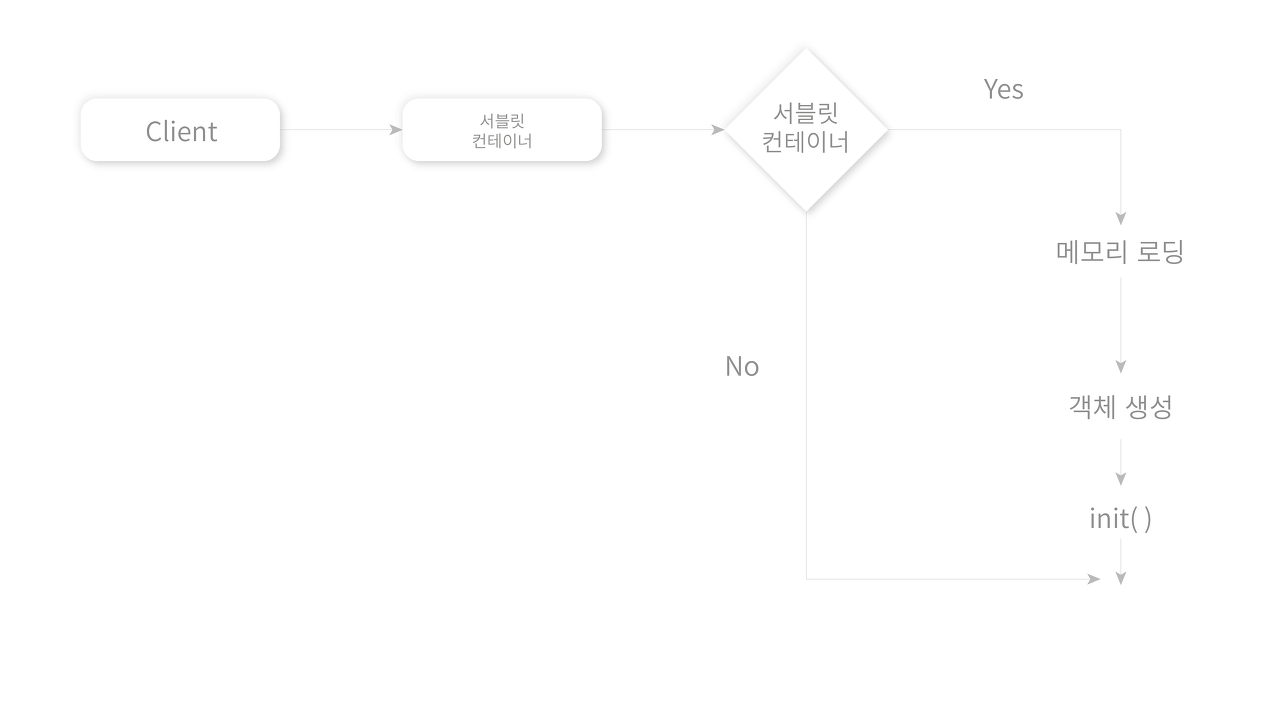
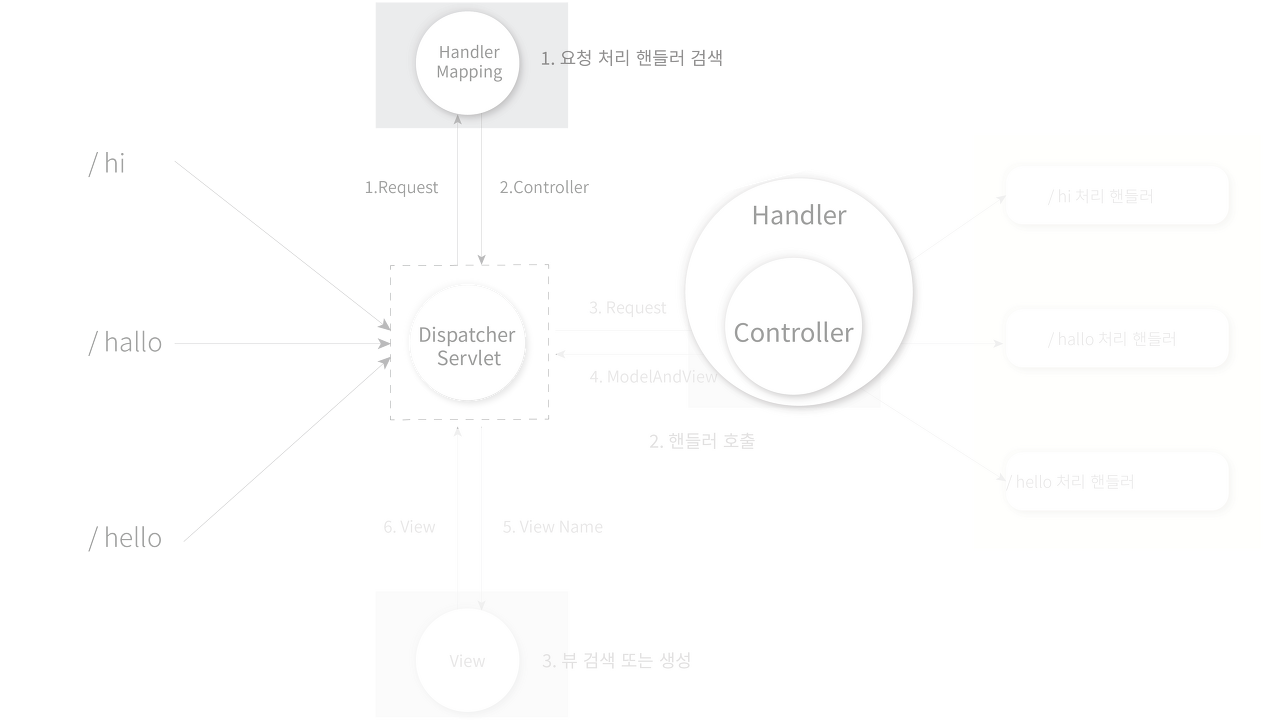
그림으로 보면 아래와 같습니다. 최초 요청이 들어와 init 메서드가 실행되고 객체들이 초기화되는 것입니다. 이렇게 한 번 초기화된 객체들은 매번 새로 생성되지 않고 스프링 컨테이너에서 재사용됩니다.
1-2. initHandlerMappings, initHandlerAdapters
여러 메서드를 호출하며 필드를 초기화하지만 컨트롤러의 동작 과정을 살펴보는 글이기 때문에 initHandlerMappings와 initHandlerAdapters 메서드가 초기화되는 과정만 살펴보겠습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
/**
* 초기화 메서드가 실행되며 DispatcherServlet의
* 아래와 같은 필드들이 초기화 됩니다.
**/
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
......
@Nullable
private static Properties defaultStrategies;
private boolean detectAllHandlerMappings = true;
private boolean detectAllHandlerAdapters = true;
private boolean detectAllHandlerExceptionResolvers = true;
private boolean detectAllViewResolvers = true;
private boolean throwExceptionIfNoHandlerFound = false;
private boolean cleanupAfterInclude = true;
@Nullable
private MultipartResolver multipartResolver;
@Nullable
private LocaleResolver localeResolver;
@Nullable
private ThemeResolver themeResolver;
@Nullable
private List<HandlerMapping> handlerMappings;
@Nullable
private List<HandlerAdapter> handlerAdapters;
@Nullable
private List<HandlerExceptionResolver> handlerExceptionResolvers;
@Nullable
private RequestToViewNameTranslator viewNameTranslator;
@Nullable
private FlashMapManager flashMapManager;
@Nullable
private List<ViewResolver> viewResolvers;
private boolean parseRequestPath;
......
}
우선 initHandlerMappings 메서드입니다. 이는 BeanFactoryUtils에서 HandlerMapping과 관련된 빈들을 Map 형태로 조회한 후 값들을 리스트에 담아 handlerMappings 필드를 초기화합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
......
@Nullable
private List<HandlerMapping> handlerMappings;
......
private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerMappings = null;
if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) {
// BeanFactoryUtils에서 HandlerMapping의 구현체를 조회
Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
// HandlerMapping의 구현체들이 존재한다면 해당 객체들을 리스트에 담아 handlerMappings 초기화
this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);
}
}
else {
try {
HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
}
}
......
}
......
}
beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors 메서드는 이름에서도 알 수 있듯 모든 계층 구조를 뒤져 하위 클래스들을 담아오는 메서드입니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
public abstract class BeanFactoryUtils {
......
public static <T> Map<String, T> beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(
ListableBeanFactory lbf, Class<T> type, boolean includeNonSingletons, boolean allowEagerInit)
throws BeansException {
Assert.notNull(lbf, "ListableBeanFactory must not be null");
Map<String, T> result = new LinkedHashMap<>(4);
result.putAll(lbf.getBeansOfType(type, includeNonSingletons, allowEagerInit));
if (lbf instanceof HierarchicalBeanFactory) {
HierarchicalBeanFactory hbf = (HierarchicalBeanFactory) lbf;
if (hbf.getParentBeanFactory() instanceof ListableBeanFactory) {
Map<String, T> parentResult = beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(
(ListableBeanFactory) hbf.getParentBeanFactory(), type, includeNonSingletons, allowEagerInit);
parentResult.forEach((beanName, beanInstance) -> {
if (!result.containsKey(beanName) && !hbf.containsLocalBean(beanName)) {
result.put(beanName, beanInstance);
}
});
}
}
return result;
}
......
}
Return all beans of the given type or subtypes, also picking up beans defined in ancestor bean factories if the current bean factory is a HierarchicalBeanFactory. The returned Map will only contain beans of this type. Does consider objects created by FactoryBeans if the “allowEagerInit” flag is set, which means that FactoryBeans will get initialized. If the object created by the FactoryBean doesn’t match, the raw FactoryBean itself will be matched against the type. If “allowEagerInit” is not set, only raw FactoryBeans will be checked (which doesn’t require initialization of each FactoryBean).
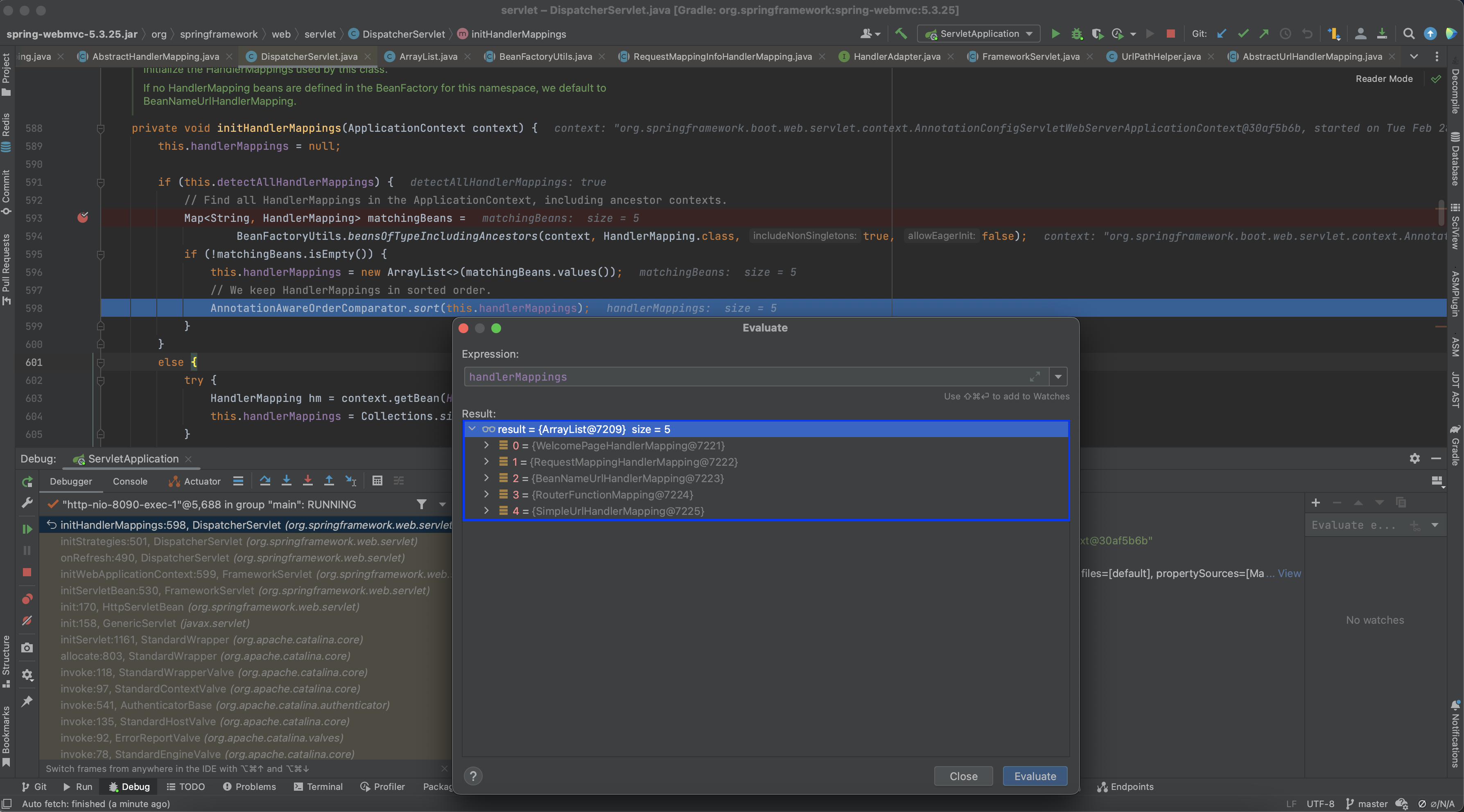
초기화된 handlerMappings 필드를 보면 WelcomePageHandlerMapping, RequestMappingHandlerMapping, BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping, RouterFunctionMapping, SimpleUrlHandlerMapping 객체들이 있는 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
해당 클래스들은 아래와 같은 역할을 맡고 있는 HandlerMapping의 구현체들입니다.
| 클래스 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| RequestMappingHandlerMapping | @Controller가 붙어있는 클래스의 메서드 레벨에서 @RequestMapping 어노테이션을 읽어 RequestMappingInfo 인스턴스를 생성합니다. |
| BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping | URL에서 이름이 슬래시(“/”)로 시작하는 빈과 매핑해주는 HandlerMapping의 구현 클래스. 매핑은 URL에서 bean 이름으로 이루어집니다. |
| WelcomePageHandlerMapping | 정적 페이지와 페이지 템플릿을 컨트롤러와 매핑시키는 HandlerMapping의 구현 클래스 |
| RouterFunctionMapping | 하나 이상의 RouterFunction bean을 감지하고 RouterFunction.andOther를 통해 결합하고 결과로 구성된 RouterFunction으로 요청을 라우팅합니다. |
| SimpleUrlHandlerMapping | 원하는 URL을 특정 핸들러에 직접 연결할 때 사용하는 설정 기반의 클래스 입니다. |
스프링 3.1 이후부터 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 이 기본 HandlerMapping이 되며 DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping이 deprecated 되었습니다.
HandlerMapping은 계층 구조를 가지고 있는데 이는 DispatcherServlet의 실행에서도 계속해서 등장하기 때문에 잘 알아둬야 합니다. 이는 위 클래스 외에도 하위 구현체로 추상 클래스인 AbstractHandlerMapping를 가지고 있으며 여기서 getHandler 메서드를 호출합니다.
getHandler 메서드가 어떻게 실행되는지는 뒷 부분에서 자세히 다루겠습니다.
이 중 대표적으로 많이 사용되는 것은 RequestMappingHandlerMapping인데 이는 @Controller가 붙은 클래스의 @RequestMapping 어노테이션을 읽어 RequestMappingInfo 객체를 생성한 후 MappingRegistry의 registry 필드에 등록합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
public class RequestMappingHandlerMapping extends RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping
implements MatchableHandlerMapping, EmbeddedValueResolverAware {
......
@Override
@Nullable
protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType) {
RequestMappingInfo info = createRequestMappingInfo(method);
if (info != null) {
RequestMappingInfo typeInfo = createRequestMappingInfo(handlerType);
if (typeInfo != null) {
info = typeInfo.combine(info);
}
String prefix = getPathPrefix(handlerType);
if (prefix != null) {
info = RequestMappingInfo.paths(prefix).options(this.config).build().combine(info);
}
}
return info;
}
......
@Nullable
private RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(AnnotatedElement element) {
RequestMapping requestMapping = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(element, RequestMapping.class);
RequestCondition<?> condition = (element instanceof Class ?
getCustomTypeCondition((Class<?>) element) : getCustomMethodCondition((Method) element));
return (requestMapping != null ? createRequestMappingInfo(requestMapping, condition) : null);
}
......
}
이 부분 또한 DispatcherServlet의 실행 2.5에서 자세하게 다루기 때문에 우선 넘어가겠습니다.
지금까지 살펴본 내용을 정리해 보면 사용자의 요청을 최초로 받으면 DispatcherServlet은 onRefresh 메서드를 실행시키고 onRefresh 메서드 내부에서 initStrategies 메서드를 호출합니다. 이 과정에서 initHandlerMappings 메서드가 호출되는데, 해당 메서드는 ApplicationContext로부터 HandlerMapping과 관련된 빈들을 조회해 DispatcherServlet의 handlerMappings 필드를 초기화합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
......
@Nullable
private List<HandlerMapping> handlerMappings;
......
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
// HandlerMapping 초기화
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
......
// 해당 메서드를 실행하며 handlerMappings 초기화
private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {
......
}
......
}
다음으로 initHandlerAdapters 메서드를 살펴보겠습니다. 이는 initHandlerMappings 메서드와 거의 유사하기 때문에 이해하는데 큰 어려움이 없을 것입니다. initHandlerAdapters 메서드도 BeanFactoryUtils의 beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors 메서드를 통해 HandlerAdapter의 빈들을 모두 가져와 handlerAdapters 필드를 초기화합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
......
private void initHandlerAdapters(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerAdapters = null;
if (this.detectAllHandlerAdapters) {
// BeanFactoryUtils에서 HandlerAdapter의 구현체를 조회
Map<String, HandlerAdapter> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerAdapter.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
// HandlerMapping의 구현체들이 존재한다면 해당 객체들을 리스트에 담아 handlerMappings 초기화
this.handlerAdapters = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerAdapters);
}
}
else {
try {
HandlerAdapter ha = context.getBean(HANDLER_ADAPTER_BEAN_NAME, HandlerAdapter.class);
this.handlerAdapters = Collections.singletonList(ha);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
}
}
......
}
......
}
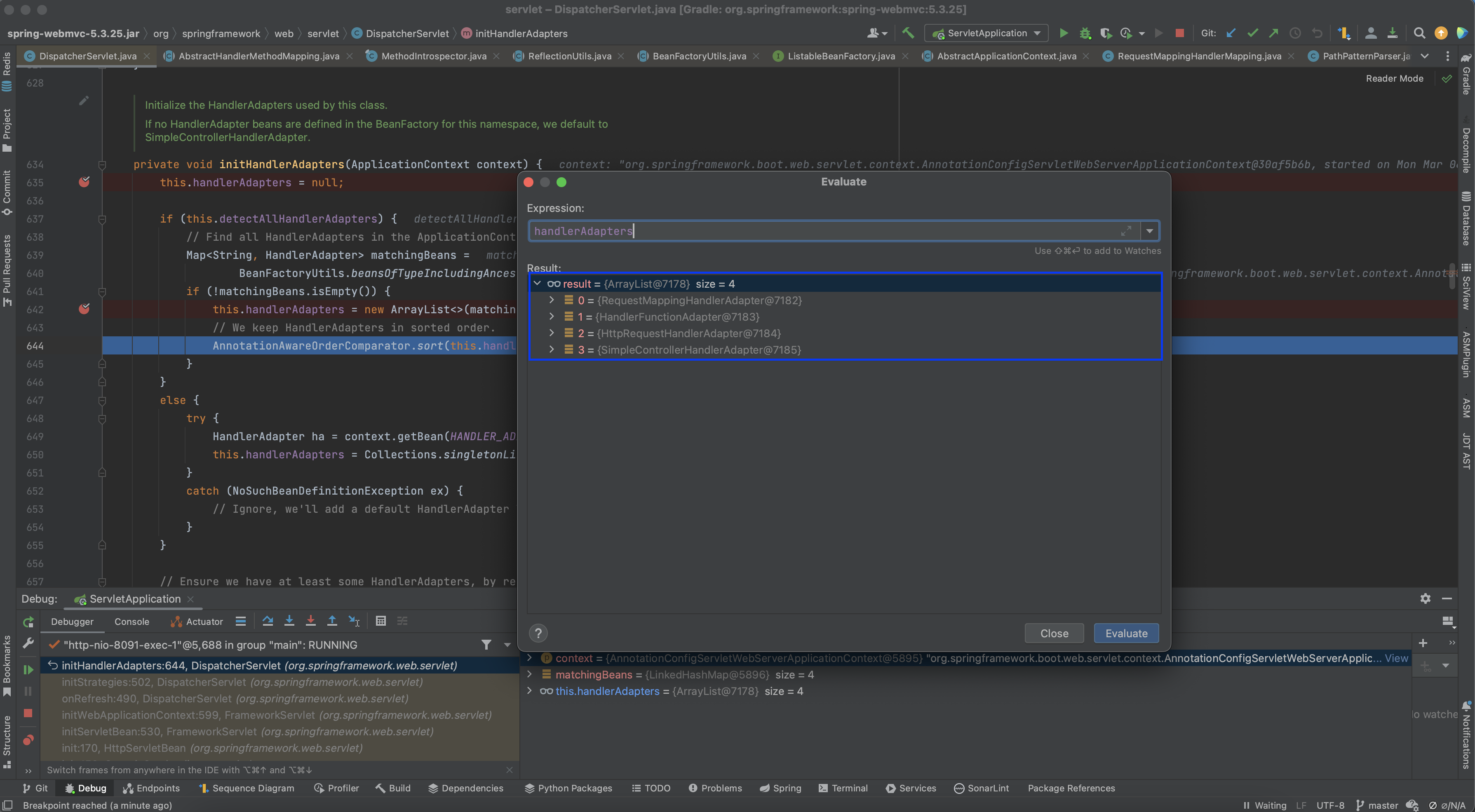
초기화된 handlerAdapters 필드를 보면 RequestMappingHandlerMappingAdapter, HandlerFunctionAdapter, HttpRequestHandlerAdapter, SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter 객체들이 있는 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
해당 클래스들은 아래와 같은 역할을 맡고 있는 HandlerAdapter의 구현체들입니다.
| 클래스 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| RequestMappingHandlerMappingAdapter | AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter를 상속하고 있으며 @RequestMapping 어노테이션이 달린 HandlerMethod를 지원합니다. |
| HandlerFunctionAdapter | HandlerHandlerFunctions를 지원하는 어댑터 구현체 |
| HttpRequestHandlerAdapter | HttpRequestHandler 인터페이스를 Generic DispatcherServlet과 함께 사용하기 위한 어댑터. LastModified 인터페이스를 서포트하기 위한 핸들러 입니다. |
| SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter | Generic DispatcherServlet과 함께 일반 컨트롤러 워크플로우 인터페이스를 사용하는 어댑터. LastModified 인터페이스를 서포트하기 위한 핸들러 입니다. |
대표적으로 많이 사용되는 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter를 살펴보겠습니다. 이는 내부적으로 handleInternal 메서드를 호출하며 이를 통해 실제 메서드를 실행하게 됩니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
public class RequestMappingHandlerAdapter extends AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter
implements BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean {
......
@Override
protected ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
ModelAndView mav;
checkRequest(request);
if (this.synchronizeOnSession) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session);
synchronized (mutex) {
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
if (!response.containsHeader(HEADER_CACHE_CONTROL)) {
if (getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod).hasSessionAttributes()) {
applyCacheSeconds(response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers);
}
else {
prepareResponse(response);
}
}
return mav;
}
......
}
handleInternal 메서드 또한 뒷 부분에서 상세하게 다루기 때문에 여기서는 넘어가도록 하겠습니다.
이는 AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter의 handle 메서드 내부에서 호출됩니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter extends WebContentGenerator implements HandlerAdapter, Ordered {
......
@Override
public final boolean supports(Object handler) {
return (handler instanceof HandlerMethod && supportsInternal((HandlerMethod) handler));
}
@Override
@Nullable
public final ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
return handleInternal(request, response, (HandlerMethod) handler);
}
.......
}
또 한 가지 살펴볼 부분은 initControllerAdviceCache입니다. 해당 메서드 내부를 살펴보면 ControllerAdvice가 붙은 클래스를 찾아 이를 초기화하는 것을 볼 수 있습니다. 즉 우리가 ExceptionHandler로 catch 하는 부분들이 여기서 초기화되는 것입니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
public class RequestMappingHandlerAdapter extends AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter
implements BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean {
......
private void initControllerAdviceCache() {
if (getApplicationContext() == null) {
return;
}
List<ControllerAdviceBean> adviceBeans = ControllerAdviceBean.findAnnotatedBeans(getApplicationContext());
List<Object> requestResponseBodyAdviceBeans = new ArrayList<>();
for (ControllerAdviceBean adviceBean : adviceBeans) {
Class<?> beanType = adviceBean.getBeanType();
if (beanType == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unresolvable type for ControllerAdviceBean: " + adviceBean);
}
Set<Method> attrMethods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(beanType, MODEL_ATTRIBUTE_METHODS);
if (!attrMethods.isEmpty()) {
this.modelAttributeAdviceCache.put(adviceBean, attrMethods);
}
Set<Method> binderMethods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(beanType, INIT_BINDER_METHODS);
if (!binderMethods.isEmpty()) {
this.initBinderAdviceCache.put(adviceBean, binderMethods);
}
if (RequestBodyAdvice.class.isAssignableFrom(beanType) || ResponseBodyAdvice.class.isAssignableFrom(beanType)) {
requestResponseBodyAdviceBeans.add(adviceBean);
}
}
......
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
public class ControllerAdviceBean implements Ordered {
......
public static List<ControllerAdviceBean> findAnnotatedBeans(ApplicationContext context) {
ListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context;
if (context instanceof ConfigurableApplicationContext) {
beanFactory = ((ConfigurableApplicationContext) context).getBeanFactory();
}
List<ControllerAdviceBean> adviceBeans = new ArrayList<>();
for (String name : BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(beanFactory, Object.class)) {
if (!ScopedProxyUtils.isScopedTarget(name)) {
ControllerAdvice controllerAdvice = beanFactory.findAnnotationOnBean(name, ControllerAdvice.class);
if (controllerAdvice != null) {
adviceBeans.add(new ControllerAdviceBean(name, beanFactory, controllerAdvice));
}
}
}
OrderComparator.sort(adviceBeans);
return adviceBeans;
}
......
}
다시 돌아와서 DispatcherServlet의 초기화 과정에 대해 마지막으로 정리해 보겠습니다. 사용자의 요청을 최초로 받으면 DispatcherServlet은 onRefresh 메서드를 실행하고 onRefresh 메서드 내부에서 initStrategies 메서드를 호출합니다. 이 과정에서 initHandlerMappings, initHandlerAdapters 등과 같은 초기화 메서드가 호출되는데, 해당 메서드는 ApplicationContext로부터 관련된 빈들을 조회해 DispatcherServlet의 필드를 초기화합니다.
- 사용자 최초 요청 시 onRefresh 메서드 호출
- onRefresh 메서드 내부에서 initStrategies 메서드 호출
- initStrategies 메서드 내부에서 아래와 같은 각 필드 초기화 메서드 호출
- DispatcherServlet의 필드 초기화 후 doService 메서드 실행
2. DispatcherServlet 실행
DispatcherServlet 내부의 초기화 과정을 살펴보았으니 DispatcherServlet이 실행되는 과정을 살펴보겠습니다.
2-1. doService, doDispatch
초기화된 DispatcherServlet은 사용자의 요청을 받으면 doService 메서드를 호출하며, 이는 내부적으로 다시 doDispatch 메서드를 호출합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
......
@Override
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
logRequest(request);
......
try {
/**
* doDispatch 호출
* */
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
......
}
}
......
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
......
try {
......
try {
......
// Handler 조회
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// HandlerAdapter 조회
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
......
// 메서드 실행 전 인터셉터 동작
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// 핸들러 메서드 호출
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
......
// 메서드 실행 후 인터셉터 동작
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
......
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
......
}
......
}
DispatcherServlet은 프론트 컨트롤러 패턴(FrontController Pattern)을 사용해 진입점을 하나로 만들고 서블릿을 재활용합니다. 이 부분에 대해서는 별도로 학습해 보실 것을 권장 드립니다.
2-2. getHandler
다시 돌아와서 doDispatch 메서드는 내부적으로 getHandler 메서드를 호출하는데 이는 HandlerMapping 리스트를 순회하며 요청 정보(URL, METHOD)에 맞는 핸들러를 찾고 필요한 인터셉터를 추가해 HandlerExecutionChain을 반환합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
......
@Nullable
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
......
}
getHandler 메서드는 핸들러 객체(컨트롤러)를 찾아오는 메서드입니다.
HandlerExecutionChain 내부에는 핸들러와 인터셉터 목록이 들어있습니다. 이는 인터셉터가 등록되어 있다면 인터셉터를 실행 후 컨트롤러의 메서드가 수행되도록 하며, 만약 없다면 바로 컨트롤러를 실행합니다. 우리가 컨트롤러 호출 전 인터셉터로 선행 작업을 할 수 있는 것은 HandlerExecutionChain 내부에 어떤 컨트롤러가 어떤 인터셉터를 가졌는지 알고 있기 때문입니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
public class HandlerExecutionChain {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(HandlerExecutionChain.class);
private final Object handler;
private final List<HandlerInterceptor> interceptorList = new ArrayList<>();
private int interceptorIndex = -1;
......
/**
* 인터셉터는 컨트롤러 앞단에 위치하는데 HandlerExecutionChain을 통해
* 컨트롤러에 요청이 도달하기 전 요청을 수행할 수 있습니다. 프론트 컨트롤러
* 패턴에서 봤던 것과 유사한 preHandler, postHandler, afterCompletion과
* 같은 메서드를 볼 수 있습니다.
* */
boolean applyPreHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
for (int i = 0; i < this.interceptorList.size(); i++) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = this.interceptorList.get(i);
if (!interceptor.preHandle(request, response, this.handler)) {
triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
return false;
}
this.interceptorIndex = i;
}
return true;
}
void applyPostHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable ModelAndView mv)
throws Exception {
for (int i = this.interceptorList.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = this.interceptorList.get(i);
interceptor.postHandle(request, response, this.handler, mv);
}
}
void applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
for (int i = this.interceptorList.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = this.interceptorList.get(i);
if (interceptor instanceof AsyncHandlerInterceptor) {
try {
AsyncHandlerInterceptor asyncInterceptor = (AsyncHandlerInterceptor) interceptor;
asyncInterceptor.afterConcurrentHandlingStarted(request, response, this.handler);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Interceptor [" + interceptor + "] failed in afterConcurrentHandlingStarted", ex);
}
}
}
}
}
......
}
2-3. getHandlerInternal
getHandler 메서드는 내부적으로 getHandlerInternal 메서드를 호출합니다. 이는 우리의 요청 정보(URL, METHOD)를 토대로 가장 적합한 HandlerMethod를 반환해 줍니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMapping extends WebApplicationObjectSupport
implements HandlerMapping, Ordered, BeanNameAware {
......
@Override
@Nullable
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// Handler 조회
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
......
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
......
return executionChain;
}
......
}
2.4 initLookupPath
getHandlerInternal 메서드는 내부에서 initLookupPath 메서드를 호출해 요청 객체로부터 사용자의 요청 URL을 파악합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
......
@Override
@Nullable
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 사용자 요청 URL 획득
String lookupPath = initLookupPath(request);
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
}
finally {
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
}
......
}
initLookupPath 메서드는 사용자 요청으로부터 요청 URL을 얻어 정제/가공한 후 반환해 줍니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMapping extends WebApplicationObjectSupport
implements HandlerMapping, Ordered, BeanNameAware {
......
protected String initLookupPath(HttpServletRequest request) {
if (usesPathPatterns()) {
request.removeAttribute(UrlPathHelper.PATH_ATTRIBUTE);
RequestPath requestPath = ServletRequestPathUtils.getParsedRequestPath(request);
String lookupPath = requestPath.pathWithinApplication().value();
return UrlPathHelper.defaultInstance.removeSemicolonContent(lookupPath);
}
else {
return getUrlPathHelper().resolveAndCacheLookupPath(request);
}
}
......
}
Initialize the path to use for request mapping. When parsed patterns are enabled a parsed RequestPath is expected to have been parsed externally by the org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet or org.springframework.web.filter.ServletRequestPathFilter. Otherwise for String pattern matching via PathMatcher the path is resolved by this method.
그 후 lookupHandlerMethod 메서드에 URL과 사용자 요청 객체를 함께 전달해 호출하고 그 결과로 HandlerMethod를 얻어냅니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
......
@Override
@Nullable
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 사용자 요청 URL 획득
String lookupPath = initLookupPath(request);
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try {
// 사용자 요청 URL을 바탕으로 HandlerMethod 획득
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
}
finally {
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
}
......
}
2-5. lookupHandlerMethod
lookupHandlerMethod 메서드를 보기 전 MappingRegistry, RequestMappingInfo, Match 등과 같은 알아야 할 몇 가지 클래스가 있는데 이에 대해 간단하게 정리 후 로직을 살펴보겠습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
......
@Nullable
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<>();
List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByDirectPath(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().keySet(), matches, request);
}
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (matches.size() > 1) {
Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));
matches.sort(comparator);
bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(matches.size() + " matching mappings: " + matches);
}
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
for (Match match : matches) {
if (match.hasCorsConfig()) {
return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH;
}
}
}
else {
Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
Method m1 = bestMatch.getHandlerMethod().getMethod();
Method m2 = secondBestMatch.getHandlerMethod().getMethod();
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Ambiguous handler methods mapped for '" + uri + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");
}
}
}
request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE, bestMatch.getHandlerMethod());
handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
return bestMatch.getHandlerMethod();
}
else {
return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().keySet(), lookupPath, request);
}
}
......
}
MappingRegistry는 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 클래스 내부에 존재하며 Handler Method에 대한 모든 매핑을 유지/관리하는 클래스입니다. 이는 동시성을 보장하며 사용자 요청 URL에 맞는 객체를 찾아주는 lookup을 수행합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
......
class MappingRegistry {
private final Map<T, MappingRegistration<T>> registry = new HashMap<>();
private final MultiValueMap<String, T> pathLookup = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
......
}
A registry that maintains all mappings to handler methods, exposing methods to perform lookups and providing concurrent access.
내부에는 Map 자료구조를 가진 여러 멤버 변수들이 있습니다. 여기서 registry, pathLookup 두 가지 필드에 대해서만 살펴보겠습니다. 우선 pathLookup 필드입니다. 이는 LinkedMultiValueMap을 사용하는데 한 개의 key에 여러 value들을 저장하는 자료구조입니다. 같은 URL이라도 GET/POST/DELETE와 같이 요청 메서드가 다를 수 있기 때문에 해당 자료구조를 사용합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
......
class MappingRegistry {
private final Map<T, MappingRegistration<T>> registry = new HashMap<>();
private final MultiValueMap<String, T> pathLookup = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
private final Map<String, List<HandlerMethod>> nameLookup = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final Map<HandlerMethod, CorsConfiguration> corsLookup = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final ReentrantReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
public Map<T, MappingRegistration<T>> getRegistrations() {
return this.registry;
}
......
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public class LinkedMultiValueMap<K, V> extends MultiValueMapAdapter<K, V> // new public base class in 5.3
implements Serializable, Cloneable {
......
public LinkedMultiValueMap(Map<K, List<V>> otherMap) {
super(new LinkedHashMap<>(otherMap));
}
......
}
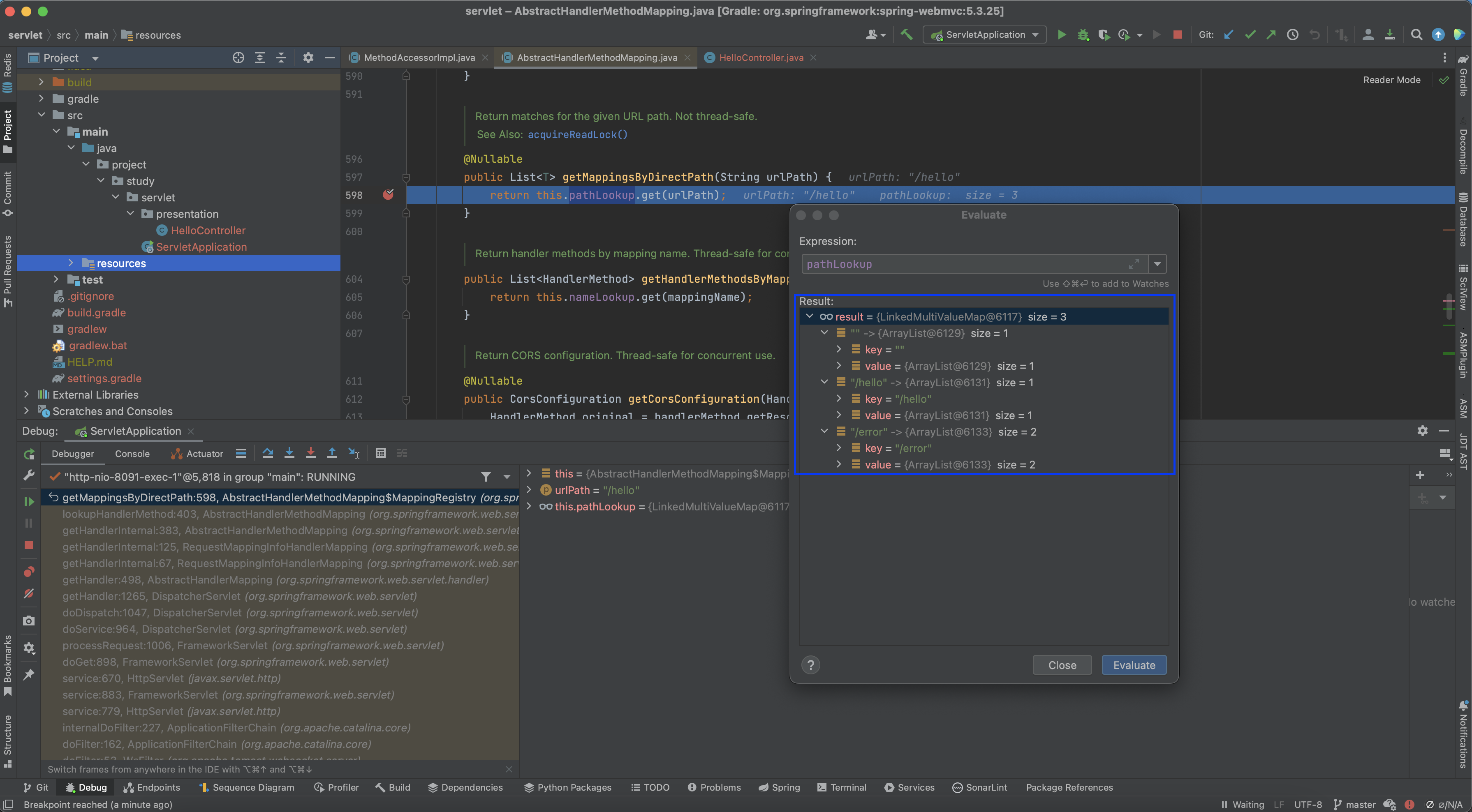
pathLookup은 key로 URL을 value에는 RequestMappingInfo를 가집니다. 즉 이를 통해 사용자가 요청한 URL에 맞는 RequestMappingInfo 객체를 꺼낼 수 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
......
class MappingRegistry {
private final Map<T, MappingRegistration<T>> registry = new HashMap<>();
/**
* Key: URL
* Description: 사용자가 요청한 URL 정보
*
* Value: RequestMappingInfo
* Description: 컨트롤러에 매핑 된 @RequestMapping에 대한 정보를 담고 있는 객체
* */
private final MultiValueMap<String, T> pathLookup = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
private final Map<String, List<HandlerMethod>> nameLookup = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final Map<HandlerMethod, CorsConfiguration> corsLookup = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final ReentrantReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
public Map<T, MappingRegistration<T>> getRegistrations() {
return this.registry;
}
......
}
}
디버깅을 해보면 key로 URL을, value로 RequestMappingInfo 객체를 가진 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
다음으로는 registry 필드입니다. 여기에는 key/value 형태로 각각 RequestMappingInfo, MappingRegistration을 저장합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
......
class MappingRegistry {
/**
* Key: RequestMappingInfo
* Description: Http Method와 URI, 파라미터 등의 정보
*
* Value: MappingRegistration
* Description: RequestMappingInfo, HandlerMethod 등의 정보
* */
private final Map<T, MappingRegistration<T>> registry = new HashMap<>();
private final MultiValueMap<String, T> pathLookup = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
private final Map<String, List<HandlerMethod>> nameLookup = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final Map<HandlerMethod, CorsConfiguration> corsLookup = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final ReentrantReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
......
}
}
MappingRegistration은 registry 필드 value에 저장되는 클래스로 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 내부에 존재합니다. 내부에는 mapping(URL 정보), handlerMethod(메서드 정보) 등과 같은 필드들이 존재합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
......
static class MappingRegistration<T> {
private final T mapping;
private final HandlerMethod handlerMethod;
private final Set<String> directPaths;
@Nullable
private final String mappingName;
private final boolean corsConfig;
public MappingRegistration(T mapping, HandlerMethod handlerMethod,
@Nullable Set<String> directPaths, @Nullable String mappingName, boolean corsConfig) {
Assert.notNull(mapping, "Mapping must not be null");
Assert.notNull(handlerMethod, "HandlerMethod must not be null");
this.mapping = mapping;
this.handlerMethod = handlerMethod;
this.directPaths = (directPaths != null ? directPaths : Collections.emptySet());
this.mappingName = mappingName;
this.corsConfig = corsConfig;
}
......
}
......
}
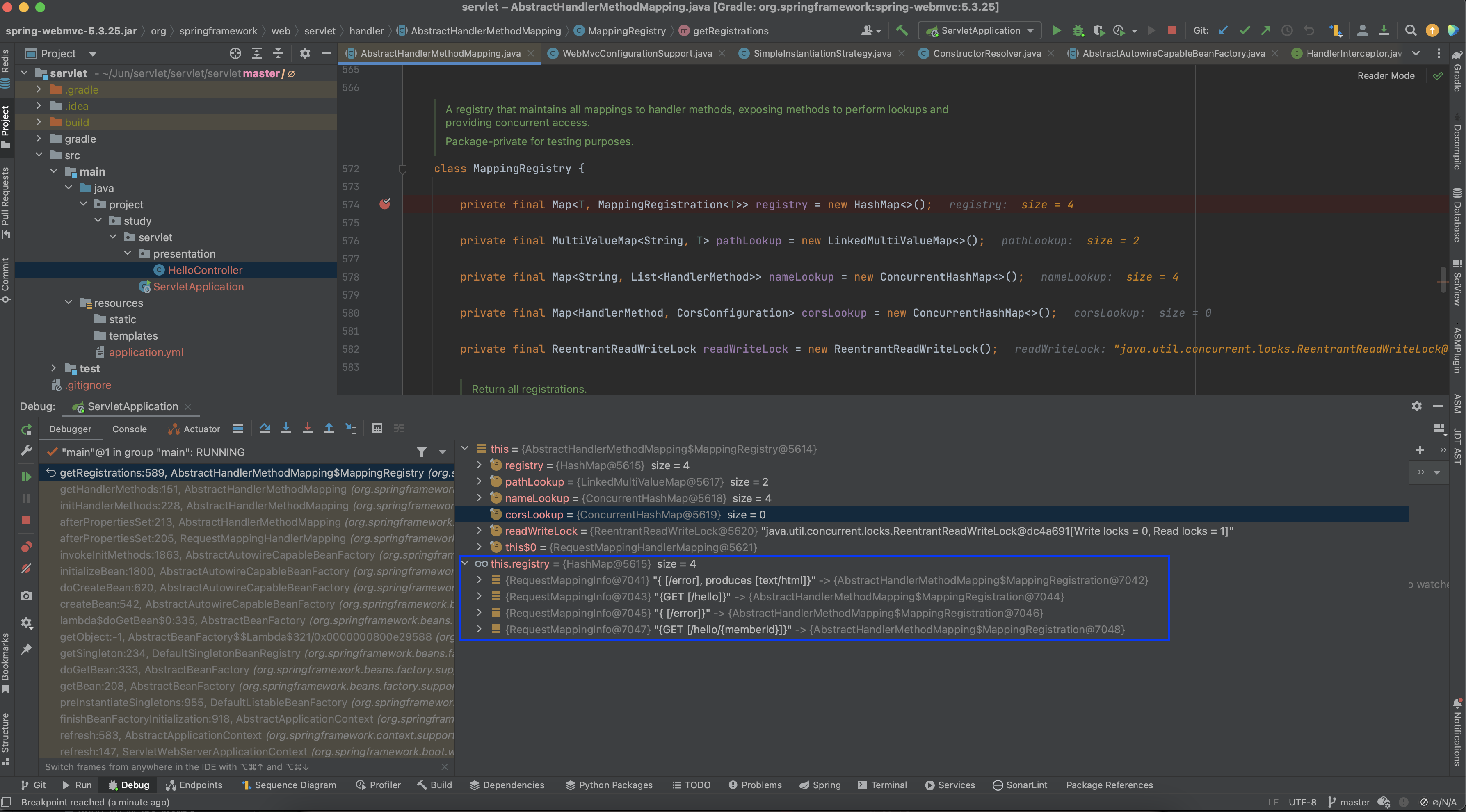
디버깅을 해보면 registry key 값으로 RequestMappingInfo, value 값으로 MappingRegistration 객체들이 들어있는 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
MappingRegistration 정보들도 한 번 확인해 보겠습니다. 위에서 봤던 URL 매핑 정보, 컨트롤러의 메서드 정보 등과 같은 값들이 들어있습니다.
다음으론 RequestMappingInfo입니다. 이는 컨트롤러에 매핑된 @RequestMapping 어노테이션을 토대로 모든 컨트롤러의 URI 정보를 가지고 있습니다. 즉 URI 패턴, 요청 메서드, consume, produce 등의 정보를 통해 해당 요청을 처리할 수 있는 메서드인지 파악할 때 사용되는 클래스입니다. 이름에서도 알 수 있듯 RequestMapping 어노테이션에 작성된 정보를 통해 만들어집니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
/**
* Request mapping information.
* Encapsulates the following request mapping conditions:
* <li>{@link PatternsRequestCondition}
* <li>{@link RequestMethodsRequestCondition}
* <li>{@link ParamsRequestCondition}
* <li>{@link HeadersRequestCondition}
* <li>{@link ConsumesRequestCondition}
* <li>{@link ProducesRequestCondition}
* <li>{@code RequestCondition} (optional, custom request condition)
*
* @author Rossen Stoyanchev
* @since 5.0
*/
public final class RequestMappingInfo implements RequestCondition<RequestMappingInfo> {
private static final PathPatternsRequestCondition EMPTY_PATH_PATTERNS = new PathPatternsRequestCondition();
private static final PatternsRequestCondition EMPTY_PATTERNS = new PatternsRequestCondition();
private static final RequestMethodsRequestCondition EMPTY_REQUEST_METHODS = new RequestMethodsRequestCondition();
private static final ParamsRequestCondition EMPTY_PARAMS = new ParamsRequestCondition();
private static final HeadersRequestCondition EMPTY_HEADERS = new HeadersRequestCondition();
private static final ConsumesRequestCondition EMPTY_CONSUMES = new ConsumesRequestCondition();
private static final ProducesRequestCondition EMPTY_PRODUCES = new ProducesRequestCondition();
private static final RequestConditionHolder EMPTY_CUSTOM = new RequestConditionHolder(null);
@Nullable
private final String name;
@Nullable
private final PathPatternsRequestCondition pathPatternsCondition;
@Nullable
private final PatternsRequestCondition patternsCondition;
private final RequestMethodsRequestCondition methodsCondition;
private final ParamsRequestCondition paramsCondition;
private final HeadersRequestCondition headersCondition;
private final ConsumesRequestCondition consumesCondition;
private final ProducesRequestCondition producesCondition;
private final RequestConditionHolder customConditionHolder;
private final int hashCode;
private final BuilderConfiguration options;
......
}
@RequestMapping에는 아래와 같은 정보가 담겨 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Mapping
public @interface RequestMapping {
String name() default "";
@AliasFor("path")
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
String[] path() default {};
RequestMethod[] method() default {};
String[] params() default {};
String[] headers() default {};
String[] consumes() default {};
String[] produces() default {};
}
이는 afterPropertiesSet 메서드 내부의 initHandlerMethods 메서드에서 핸들러를 초기화하면서 정보를 읽어오게 됩니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
......
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
initHandlerMethods();
}
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
for (String beanName : getCandidateBeanNames()) {
if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) {
processCandidateBean(beanName);
}
}
handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());
}
......
}
initHandlerMethods 내부에서 processCandidateBean 메서드를 호출하게 되는데 이는 ApplicationContext으로부터 빈 이름으로 Class 타입을 조회합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
......
protected void processCandidateBean(String beanName) {
Class<?> beanType = null;
try {
// ApplicationContext에서 빈 이름으로 조회
beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
}
......
if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) {
detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
}
}
......
이는 다시 detectHandlerMethods 메서드를 호출하게 되며, 내부에서 RequestMappingHandlerMapping에 있는 getMappingForMethod 메서드를 호출합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
......
protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler) {
Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ?
obtainApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass());
if (handlerType != null) {
Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> {
try {
// getMappingForMethod 메서드 호출
return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
......
}
});
......
methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> {
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType);
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);
});
}
}
......
}
getMappingForMethod 내부에서 createRequestMappingInfo 메서드를 호출하게 되고 여기서 RequestMappingInfo 정보를 반환해 registry에 저장하게 됩니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
public class RequestMappingHandlerMapping extends RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping
implements MatchableHandlerMapping, EmbeddedValueResolverAware {
......
@Override
@Nullable
protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType) {
RequestMappingInfo info = createRequestMappingInfo(method);
if (info != null) {
RequestMappingInfo typeInfo = createRequestMappingInfo(handlerType);
if (typeInfo != null) {
info = typeInfo.combine(info);
}
String prefix = getPathPrefix(handlerType);
if (prefix != null) {
info = RequestMappingInfo.paths(prefix).options(this.config).build().combine(info);
}
}
return info;
}
......
}
detectHandlerMethods 메서드로 다시 돌아와서 보면 마지막에 registerHandlerMethod 메서드를 호출해 registry에 값을 저장하는 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
......
protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler) {
Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ?
obtainApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass());
if (handlerType != null) {
......
// forEach를 순회하며 registerHandlerMethod 메서드 호출
methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> {
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType);
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);
});
}
}
......
// mappingRegistry에 값 저장
protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) {
this.mappingRegistry.register(mapping, handler, method);
}
......
}
마지막으로 Match 클래스입니다. 이는 현재 요청에서 가장 적절한 HandlerMethod를 찾기 위한 비교를 담당합니다. 컨트롤러에서 같은 URL을 가지고 있더라도 GET/POST/DELETE와 같이 여러 메서드를 가질 수 있기 때문에 이 중 사용자 요청에 가장 적합한 객체를 비교해 가져오기 위한 클래스입니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
......
private class Match {
private final T mapping;
private final MappingRegistration<T> registration;
public Match(T mapping, MappingRegistration<T> registration) {
this.mapping = mapping;
this.registration = registration;
}
public HandlerMethod getHandlerMethod() {
return this.registration.getHandlerMethod();
}
public boolean hasCorsConfig() {
return this.registration.hasCorsConfig();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.mapping.toString();
}
}
private class MatchComparator implements Comparator<Match> {
private final Comparator<T> comparator;
public MatchComparator(Comparator<T> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
}
@Override
public int compare(Match match1, Match match2) {
return this.comparator.compare(match1.mapping, match2.mapping);
}
}
......
}
lookupHandlerMethod 메서드를 이해하기 위해 MappingResitry, MappingRegistration, RequestMappingInfo, Match 등의 여러 객체를 살펴보았습니다. 이제 본격적으로 lookupHandlerMethod 메서드 내부를 살펴보겠습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
......
@Nullable
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<>();
// 해당 URL에 매칭되는 RequestMappingInfo 리스트 조회
List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByDirectPath(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
// 해당 RequestMappingInfo에 매칭되는 MappingRegistration 값들을 추가
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().keySet(), matches, request);
}
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (matches.size() > 1) {
// 정렬을 통해 최적의 객체 선택
Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));
matches.sort(comparator);
bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(matches.size() + " matching mappings: " + matches);
}
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
for (Match match : matches) {
if (match.hasCorsConfig()) {
return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH;
}
}
}
else {
Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
Method m1 = bestMatch.getHandlerMethod().getMethod();
Method m2 = secondBestMatch.getHandlerMethod().getMethod();
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Ambiguous handler methods mapped for '" + uri + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");
}
}
}
request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE, bestMatch.getHandlerMethod());
handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
// URL, HttpMethod 등의 정보를 비교해 가장 적합한 객체 선택 후 반환
return bestMatch.getHandlerMethod();
}
else {
return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().keySet(), lookupPath, request);
}
}
......
}
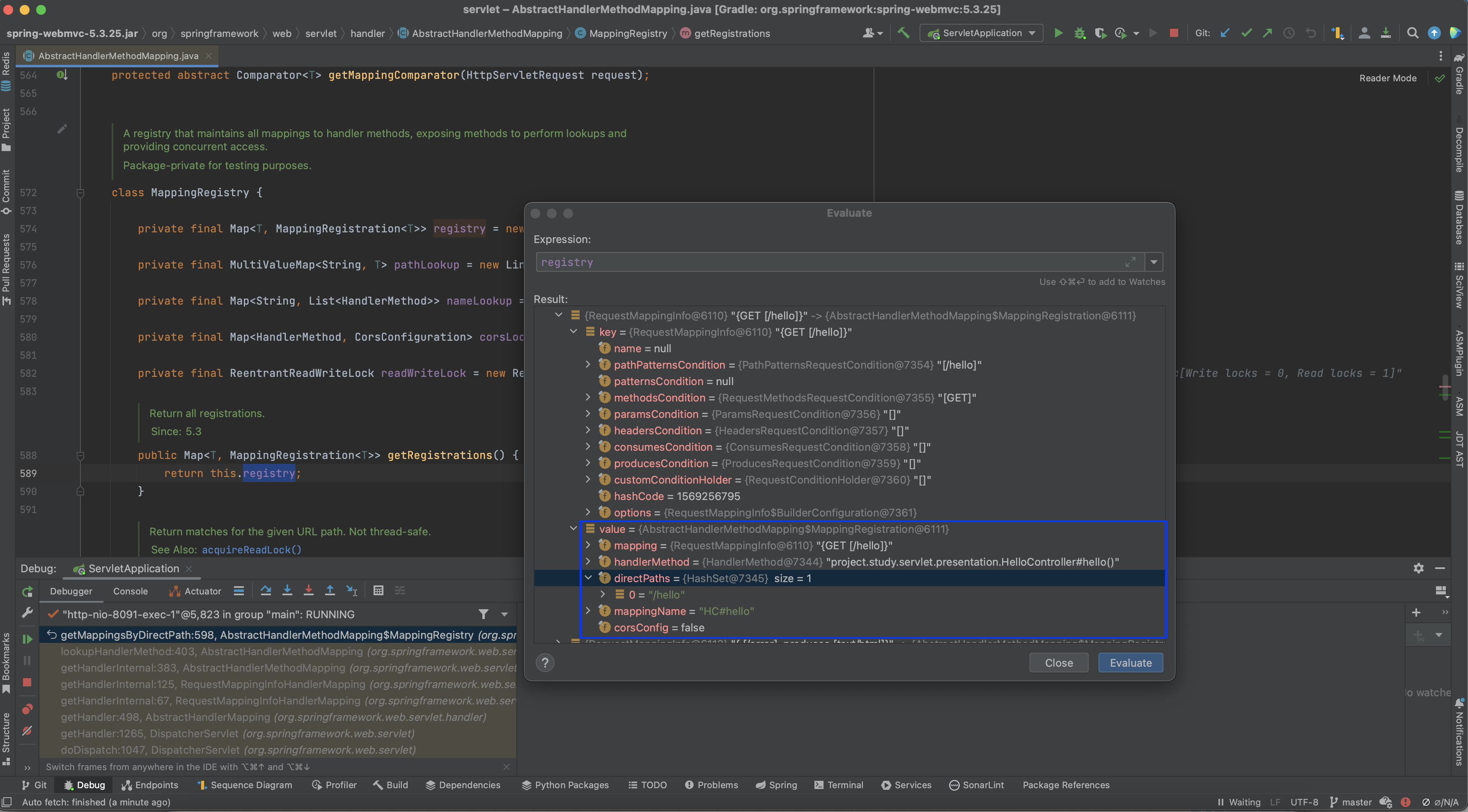
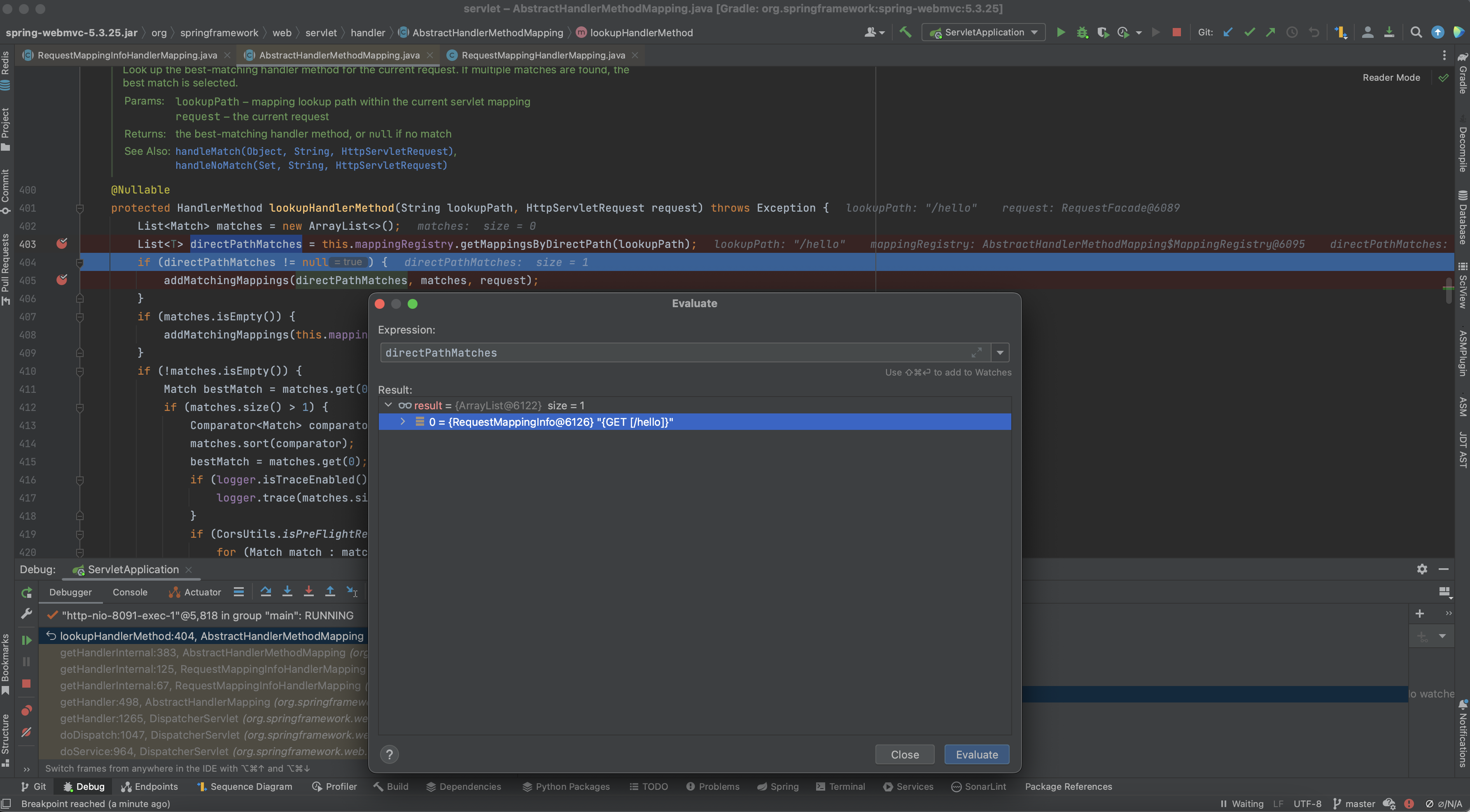
먼저 현재 사용자 요청 URL에 맞는 RequestMappingInfo 객체를 directPathMatches 메서드를 통해 찾아옵니다.
이는 MappingRegistry 내부에 존재하는 pathLookup 필드에서 사용자 URL을 통해 값을 가져옵니다. 이때 반환되는 리스트는 RequestMappingInfo 리스트입니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
......
class MappingRegistry {
private final Map<T, MappingRegistration<T>> registry = new HashMap<>();
private final MultiValueMap<String, T> pathLookup = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
.......
@Nullable
public List<T> getMappingsByDirectPath(String urlPath) {
return this.pathLookup.get(urlPath);
}
......
}
......
}
이후 URL에 매칭되는 RequestMappingInfo 리스트가 존재한다면 addMatchingMappings 메서드를 실행합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
......
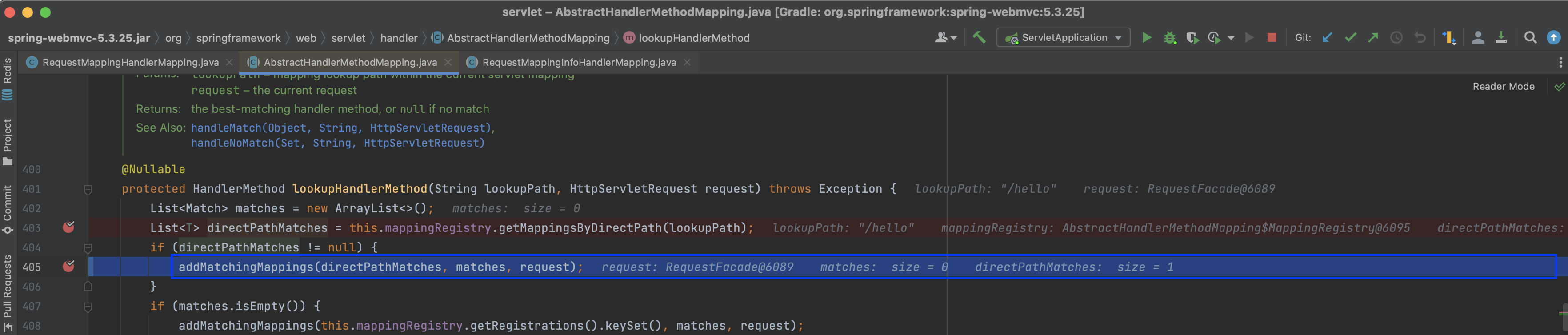
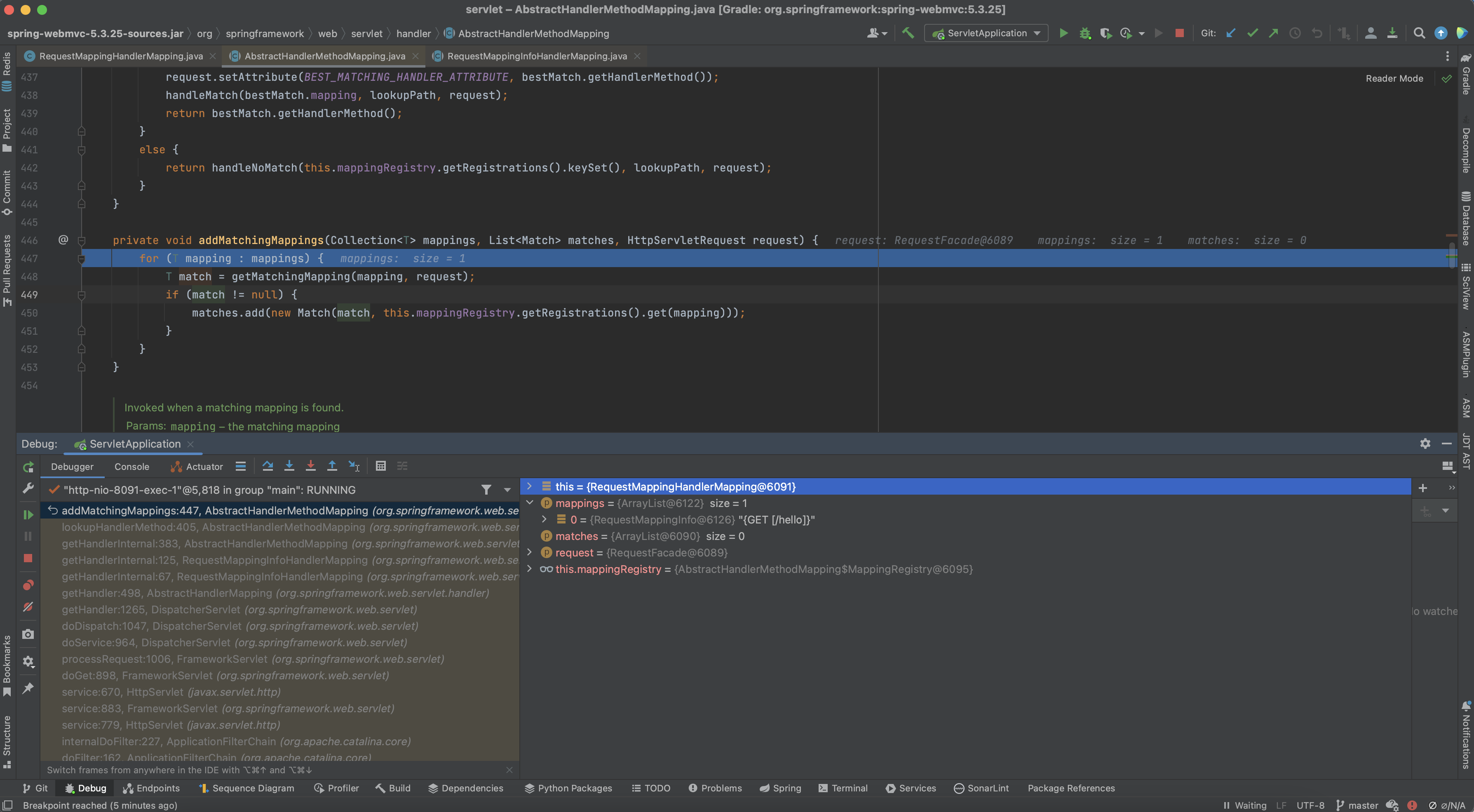
private void addMatchingMappings(Collection<T> mappings, List<Match> matches, HttpServletRequest request) {
for (T mapping : mappings) {
T match = getMatchingMapping(mapping, request);
if (match != null) {
// registry에서 RequestMappingInfo에 맞는 MappingRegistration 반환
matches.add(new Match(match, this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().get(mapping)));
}
}
}
......
}
addMatchingMappings 메서드 내부에서 RequestMappingInfo 리스트를 순회하며 matches에 값을 추가합니다. match를 추가하는 부분을 보면 Registrations에서 mapping(RequestMappingInfo)을 key 값으로 어떤 값을 조회해 오는 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
위에 나오는 Registration은 MappingRegistry 내부에 존재하는 registry이며, 해당 Map을 조회해서 RequestMappingInfo를 key로 MappingRegistration을 가져오는 것입니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
......
class MappingRegistry {
private final Map<T, MappingRegistration<T>> registry = new HashMap<>();
private final MultiValueMap<String, T> pathLookup = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
......
public Map<T, MappingRegistration<T>> getRegistrations() {
return this.registry;
}
......
}
}
메서드가 길기 때문에 여기까지 한 번 정리해 보겠습니다. 우선 사용자 요청이 오면 요청 URL을 key로 MappingRegistry의 pathLooup에서 RequestMappingInfo 객체들을 가져옵니다. 같은 URL이라도 GET/POST 등 여러 메서드가 존재하기 때문에 이 값은 리스트입니다. 이후 리스트를 순회하며 registry에서 RequestMappingInfo를 key로 MappingRegistration 값들을 가져옵니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
......
@Nullable
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<>();
// 해당 URL에 매칭되는 RequestMappingInfo 리스트 조회
List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByDirectPath(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
// 해당 RequestMappingInfo에 매칭되는 MappingRegistration 값들을 추가
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().keySet(), matches, request);
}
......
}
......
}
메서드 나머지 부분도 살펴보겠습니다. 여기서는 찾아온 matches에서 가장 적합한 객체를 찾습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
......
@Nullable
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
......
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (matches.size() > 1) {
Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));
// sort 메서드로 가장 적합한 객체 선택
matches.sort(comparator);
bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(matches.size() + " matching mappings: " + matches);
}
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
for (Match match : matches) {
if (match.hasCorsConfig()) {
return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH;
}
}
}
else {
Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
Method m1 = bestMatch.getHandlerMethod().getMethod();
Method m2 = secondBestMatch.getHandlerMethod().getMethod();
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Ambiguous handler methods mapped for '" + uri + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");
}
}
}
......
}
}
......
}
이는 lookupHandlerMethod 메서드 내부에서 handleMatch 메서드를 호출합니다. 여기서 가장 적합한 객체를 찾아 담은 후 HandlerMethod를 반환합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
......
@Nullable
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
......
request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE, bestMatch.getHandlerMethod());
handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
// URL, HttpMethod 등의 정보를 비교해 가장 적합한 객체 선택 후 반환
return bestMatch.getHandlerMethod();
}
else {
return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().keySet(), lookupPath, request);
}
}
......
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
public abstract class RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping extends AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<RequestMappingInfo> {
.......
@Override
protected void handleMatch(RequestMappingInfo info, String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) {
super.handleMatch(info, lookupPath, request);
RequestCondition<?> condition = info.getActivePatternsCondition();
if (condition instanceof PathPatternsRequestCondition) {
extractMatchDetails((PathPatternsRequestCondition) condition, lookupPath, request);
} else {
extractMatchDetails((PatternsRequestCondition) condition, lookupPath, request);
}
ProducesRequestCondition producesCondition = info.getProducesCondition();
if (!producesCondition.isEmpty()) {
Set<MediaType> mediaTypes = producesCondition.getProducibleMediaTypes();
if (!mediaTypes.isEmpty()) {
request.setAttribute(PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE, mediaTypes);
}
}
}
......
}
lookupHandlerMethod를 통해 HandlerMethod를 찾으면 getHandlerInternal 돌아와 이를 반환하며 메서드를 종료합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodMapping<T> extends AbstractHandlerMapping implements InitializingBean {
......
@Override
@Nullable
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
String lookupPath = initLookupPath(request);
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
// 찾아온 Handler를 반환
return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
}
finally {
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
}
......
}
getHandlerInternal 메서드가 반환하는 HandlerMethod에 대해서도 한 번 살펴보겠습니다. HandlerMethod는 메서드와 빈으로 구성된 핸들러 메서드에 대한 정보를 캡슐화하며 매개 변수, 반환 값, 주석 등에 대한 정보를 제공합니다.
Encapsulates information about a handler method consisting of a method and a bean. Provides convenient access to method parameters, the method return value, method annotations, etc. The class may be created with a bean instance or with a bean name (e.g. lazy-init bean, prototype bean). Use createWithResolvedBean() to obtain a HandlerMethod instance with a bean instance resolved through the associated BeanFactory.
이는 그 자체로 어떤 행위를 하기보단 메서드를 실행하기 위해 필요한 참조 정보를 담고 있는 객체입니다. 내부 필드를 보면 메서드 자체에 대한 메타정보를 담고 있는 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
public class HandlerMethod {
protected static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(HandlerMethod.class);
private final Object bean;
@Nullable
private final BeanFactory beanFactory;
@Nullable
private final MessageSource messageSource;
// 빈 타입
private final Class<?> beanType;
// 메서드
private final Method method;
private final Method bridgedMethod;
// 파라미터
private final MethodParameter[] parameters;
@Nullable
private HttpStatus responseStatus;
@Nullable
private String responseStatusReason;
@Nullable
private HandlerMethod resolvedFromHandlerMethod;
// 어노테이션 정보
@Nullable
private volatile List<Annotation[][]> interfaceParameterAnnotations;
private final String description;
......
}
2-6. getHandlerAdapter
getHandler 메서드로 핸들러를 조회해왔다면 어댑터를 얻어와야 합니다. 핸들러 어댑터는 컨트롤러에서 요청에 맞는 메서드를 실행하고 DispatcherServlet에 결과를 반환하는 클래스입니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
......
try {
......
try {
......
// Handler 조회
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// HandlerAdapter 조회
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
......
}
......
}
}
......
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
......
protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {
if (this.handlerAdapters != null) {
for (HandlerAdapter adapter : this.handlerAdapters) {
if (adapter.supports(handler)) {
return adapter;
}
}
}
throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler +
"]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler");
}
......
즉 핸들러 매핑에 의해 사용할 핸들러를 찾아주면 HandlerAdapter를 통해 컨트롤러 메서드를 실행해 줍니다. 조금 복잡할 수 있는데 컨트롤러 객체를 찾는 것과 실행을 분리한 것입니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
public interface HandlerAdapter {
boolean supports(Object handler);
@Nullable
ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception;
@Deprecated
long getLastModified(HttpServletRequest request, Object handler);
}
스프링이 지원하는 핸들러 어댑터는 아래와 같습니다. 여기서 주로 사용되는 것은 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter입니다. 이는 1.2에서 살펴보았기 때문에 넘어가겠습니다.
- RequestMappingHandlerAdapter : 애노테이션 기반의 컨트롤러인 @RequestMapping에서 사용
- HttpRequestHandlerAdapter : HttpRequestHandler 처리
- SimpleControllerHandlerAdatper : Controller 인터페이스 처리
2-7. handle
찾아온 HandlerAdapter에서 handle 메서드를 실행합니다. 여기서부터는 메서드를 연속적으로 호출하는 부분이 나오는데 이전보다는 조금 편하게 보셔도 될 것 같습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
......
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
......
try {
......
try {
......
// HandlerAdapter 조회
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
......
// 메서드 실행 전 인터셉터 동작
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// 핸들러 메서드 호출
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
......
}
......
}
}
......
}
이는 다시 내부적으로 handleInternal 메서드를 호출합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter extends WebContentGenerator implements HandlerAdapter, Ordered {
......
@Override
@Nullable
public final ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
return handleInternal(request, response, (HandlerMethod) handler);
}
......
}
2-8. handleInternal
이는 또 내부적으로 invokeHandlerMethod 메서드를 호출합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
public class RequestMappingHandlerAdapter extends AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter
implements BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean {
......
@Override
protected ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
......
if (this.synchronizeOnSession) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session);
synchronized (mutex) {
// invokeHandlerMethod 호출
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
......
return mav;
}
......
}
2-9. invokeHandlerMethod
이는 또 내부적으로 invokeAndHandle 메서드를 호출합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
public class RequestMappingHandlerAdapter extends AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter
implements BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean {
......
@Nullable
protected ModelAndView invokeHandlerMethod(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response);
try {
WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod);
ModelFactory modelFactory = getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory);
ServletInvocableHandlerMethod invocableMethod = createInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod);
// ArgumentResolver
if (this.argumentResolvers != null) {
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers);
}
......
// invokeAndHandle 메서드 호출
invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer);
......
return getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest);
}
finally {
webRequest.requestCompleted();
}
}
......
}
2-10. invokeAndHandle
이는 또 내부적으로 invokeForRequest 메서드를 호출합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
public class ServletInvocableHandlerMethod extends InvocableHandlerMethod {
......
public void invokeAndHandle(ServletWebRequest webRequest, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs);
setResponseStatus(webRequest);
if (returnValue == null) {
if (isRequestNotModified(webRequest) || getResponseStatus() != null || mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) {
disableContentCachingIfNecessary(webRequest);
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
} else if (StringUtils.hasText(getResponseStatusReason())) {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(false);
Assert.state(this.returnValueHandlers != null, "No return value handlers");
try {
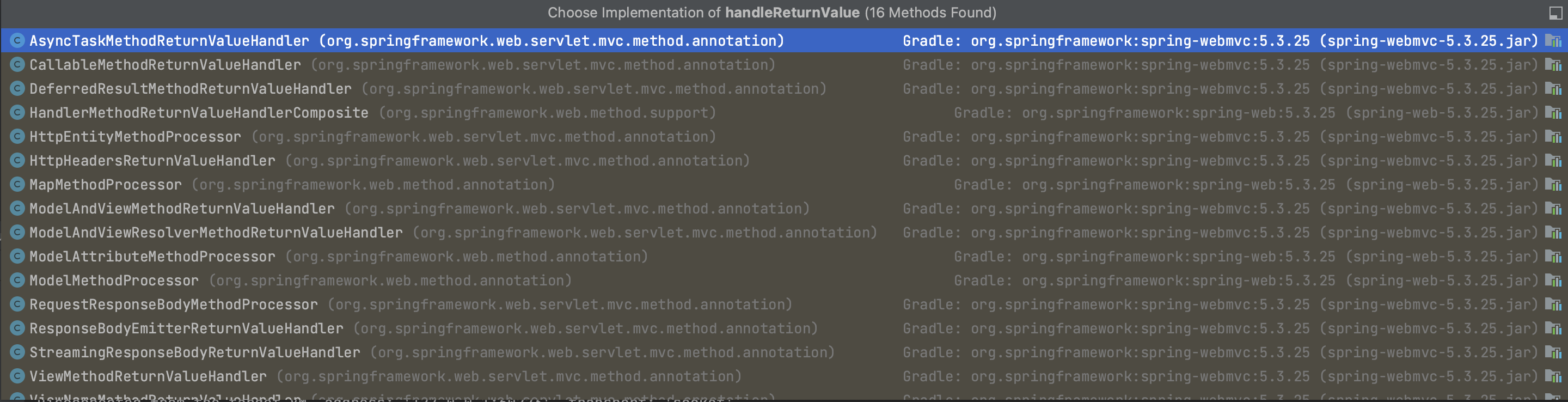
this.returnValueHandlers.handleReturnValue(
returnValue, getReturnValueType(returnValue), mavContainer, webRequest);
} catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(formatErrorForReturnValue(returnValue), ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
......
}
2-11. invokeForRequest
이는 또 내부적으로 doInvoke 메서드를 호출합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
public class InvocableHandlerMethod extends HandlerMethod {
......
@Nullable
public Object invokeForRequest(NativeWebRequest request, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
Object[] args = getMethodArgumentValues(request, mavContainer, providedArgs);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Arguments: " + Arrays.toString(args));
}
return doInvoke(args);
}
......
}
2-12. doInvoke
이는 또 내부적으로 invoke 메서드를 호출합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
public class InvocableHandlerMethod extends HandlerMethod {
......
@Nullable
protected Object doInvoke(Object... args) throws Exception {
Method method = getBridgedMethod();
try {
if (KotlinDetector.isSuspendingFunction(method)) {
return CoroutinesUtils.invokeSuspendingFunction(method, getBean(), args);
}
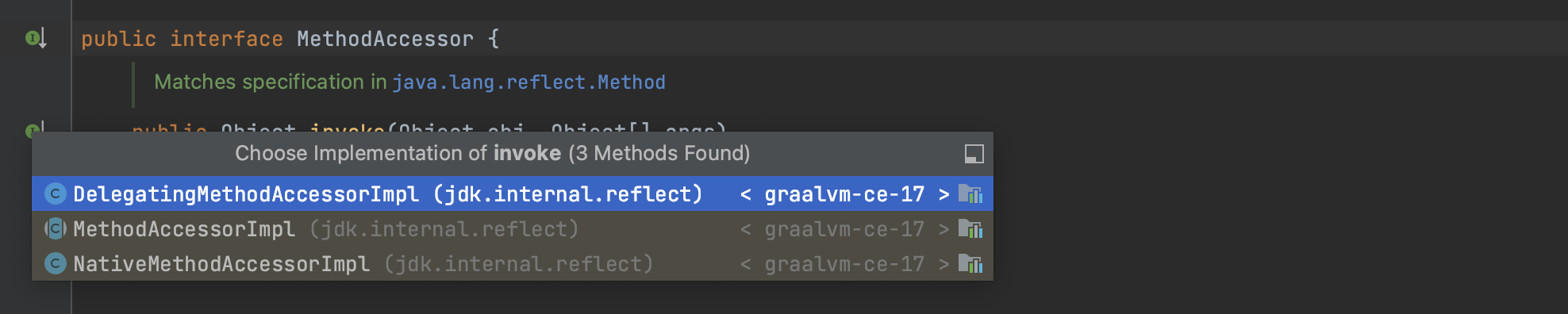
return method.invoke(getBean(), args);
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
assertTargetBean(method, getBean(), args);
String text = (ex.getMessage() != null ? ex.getMessage() : "Illegal argument");
throw new IllegalStateException(formatInvokeError(text, args), ex);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
// Unwrap for HandlerExceptionResolvers ...
Throwable targetException = ex.getTargetException();
if (targetException instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) targetException;
}
else if (targetException instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) targetException;
}
else if (targetException instanceof Exception) {
throw (Exception) targetException;
}
else {
throw new IllegalStateException(formatInvokeError("Invocation failure", args), targetException);
}
}
}
}
2-13. invoke
invoke 메서드에서 드디어 실제 메서드를 호출하게 됩니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
public final class Method extends Executable {
......
private volatile MethodAccessor methodAccessor;
......
@CallerSensitive
@ForceInline
@IntrinsicCandidate
public Object invoke(Object obj, Object... args)
throws IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException,
InvocationTargetException
{
if (!override) {
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
checkAccess(caller, clazz,
Modifier.isStatic(modifiers) ? null : obj.getClass(),
modifiers);
}
MethodAccessor ma = methodAccessor; // read volatile
if (ma == null) {
ma = acquireMethodAccessor();
}
// 메서드 호출
return ma.invoke(obj, args);
}
......
}
MethodAccessor는 인터페이스로 invoke 메서드를 가지고 있습니다. 이는 Method 내부에 필드로 존재합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
public interface MethodAccessor {
public Object invoke(Object obj, Object[] args)
throws IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
class DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl extends MethodAccessorImpl {
private MethodAccessorImpl delegate;
DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl(MethodAccessorImpl delegate) {
setDelegate(delegate);
}
public Object invoke(Object obj, Object[] args)
throws IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException
{
return delegate.invoke(obj, args);
}
void setDelegate(MethodAccessorImpl delegate) {
this.delegate = delegate;
}
}
This interface provides the declaration for java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(). Each Method object is configured with a (possibly dynamically-generated) class which implements this interface.
이는 하위 구현체로 아래와 같은 클래스를 가지고 있으며 인자로 들어온 객체의 메서드를 호출합니다.
2-14. returnValue
메서드가 종료되면 ServletInvocableHandlerMethod.invokeAndHandle 메서드 내부에서 handleReturnValue 메서드를 호출해 컨트롤러에 있는 어노테이션과 반환 타입 정보를 바탕으로 이를 처리하기 위한 HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler를 찾습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
public class ServletInvocableHandlerMethod extends InvocableHandlerMethod {
......
public void invokeAndHandle(ServletWebRequest webRequest, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs);
setResponseStatus(webRequest);
if (returnValue == null) {
if (isRequestNotModified(webRequest) || getResponseStatus() != null || mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) {
disableContentCachingIfNecessary(webRequest);
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
} else if (StringUtils.hasText(getResponseStatusReason())) {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(false);
Assert.state(this.returnValueHandlers != null, "No return value handlers");
try {
// HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler 조회
this.returnValueHandlers.handleReturnValue(
returnValue, getReturnValueType(returnValue), mavContainer, webRequest);
} catch (Exception ex) {
......
}
}
......
}
HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler는 인터페이스로 아래와 같은 구현체들을 가집니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public interface HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler {
boolean supportsReturnType(MethodParameter returnType);
void handleReturnValue(@Nullable Object returnValue, MethodParameter returnType,
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest) throws Exception;
}
구현체가 많기 때문에 @ResponseBody를 사용해 json 값을 반환한다고 가정해 보겠습니다. 이 경우 구현체 중 RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor가 사용되며 내부적으로 writeWithMessageConverters 메서드가 또 호출됩니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
public class RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor extends AbstractMessageConverterMethodProcessor {
......
@Override
public Object resolveArgument(MethodParameter parameter, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
NativeWebRequest webRequest, @Nullable WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) throws Exception {
parameter = parameter.nestedIfOptional();
Object arg = readWithMessageConverters(webRequest, parameter, parameter.getNestedGenericParameterType());
String name = Conventions.getVariableNameForParameter(parameter);
if (binderFactory != null) {
WebDataBinder binder = binderFactory.createBinder(webRequest, arg, name);
if (arg != null) {
validateIfApplicable(binder, parameter);
if (binder.getBindingResult().hasErrors() && isBindExceptionRequired(binder, parameter)) {
throw new MethodArgumentNotValidException(parameter, binder.getBindingResult());
}
}
if (mavContainer != null) {
mavContainer.addAttribute(BindingResult.MODEL_KEY_PREFIX + name, binder.getBindingResult());
}
}
return adaptArgumentIfNecessary(arg, parameter);
}
......
}
2-15. writeWithMessageConverters
드디어 길고 긴 글의 마지막입니다. writeWithMessageConverters 메서드에서 반환 타입을 정한 후 요청에 맞는 값을 반환합니다. 메서드 내부를 보면 MediaType과 같은 헤더 정보, 반환 데이터(body) 등을 체크하는 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
public abstract class AbstractMessageConverterMethodProcessor extends AbstractMessageConverterMethodArgumentResolver
implements HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler {
......
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unchecked"})
protected <T> void writeWithMessageConverters(@Nullable T value, MethodParameter returnType,
ServletServerHttpRequest inputMessage, ServletServerHttpResponse outputMessage)
throws IOException, HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException, HttpMessageNotWritableException {
Object body;
Class<?> valueType;
Type targetType;
if (value instanceof CharSequence) {
body = value.toString();
valueType = String.class;
targetType = String.class;
} else {
body = value;
valueType = getReturnValueType(body, returnType);
targetType = GenericTypeResolver.resolveType(getGenericType(returnType), returnType.getContainingClass());
}
if (isResourceType(value, returnType)) {
outputMessage.getHeaders().set(HttpHeaders.ACCEPT_RANGES, "bytes");
if (value != null && inputMessage.getHeaders().getFirst(HttpHeaders.RANGE) != null &&
outputMessage.getServletResponse().getStatus() == 200) {
Resource resource = (Resource) value;
try {
List<HttpRange> httpRanges = inputMessage.getHeaders().getRange();
outputMessage.getServletResponse().setStatus(HttpStatus.PARTIAL_CONTENT.value());
body = HttpRange.toResourceRegions(httpRanges, resource);
valueType = body.getClass();
targetType = RESOURCE_REGION_LIST_TYPE;
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
outputMessage.getHeaders().set(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_RANGE, "bytes */" + resource.contentLength());
outputMessage.getServletResponse().setStatus(HttpStatus.REQUESTED_RANGE_NOT_SATISFIABLE.value());
}
}
}
MediaType selectedMediaType = null;
MediaType contentType = outputMessage.getHeaders().getContentType();
boolean isContentTypePreset = contentType != null && contentType.isConcrete();
if (isContentTypePreset) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Found 'Content-Type:" + contentType + "' in response");
}
selectedMediaType = contentType;
} else {
HttpServletRequest request = inputMessage.getServletRequest();
List<MediaType> acceptableTypes;
try {
acceptableTypes = getAcceptableMediaTypes(request);
} catch (HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException ex) {
int series = outputMessage.getServletResponse().getStatus() / 100;
if (body == null || series == 4 || series == 5) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Ignoring error response content (if any). " + ex);
}
return;
}
throw ex;
}
List<MediaType> producibleTypes = getProducibleMediaTypes(request, valueType, targetType);
if (body != null && producibleTypes.isEmpty()) {
throw new HttpMessageNotWritableException(
"No converter found for return value of type: " + valueType);
}
List<MediaType> mediaTypesToUse = new ArrayList<>();
for (MediaType requestedType : acceptableTypes) {
for (MediaType producibleType : producibleTypes) {
if (requestedType.isCompatibleWith(producibleType)) {
mediaTypesToUse.add(getMostSpecificMediaType(requestedType, producibleType));
}
}
}
if (mediaTypesToUse.isEmpty()) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("No match for " + acceptableTypes + ", supported: " + producibleTypes);
}
if (body != null) {
throw new HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException(producibleTypes);
}
return;
}
MediaType.sortBySpecificityAndQuality(mediaTypesToUse);
for (MediaType mediaType : mediaTypesToUse) {
if (mediaType.isConcrete()) {
selectedMediaType = mediaType;
break;
} else if (mediaType.isPresentIn(ALL_APPLICATION_MEDIA_TYPES)) {
selectedMediaType = MediaType.APPLICATION_OCTET_STREAM;
break;
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Using '" + selectedMediaType + "', given " +
acceptableTypes + " and supported " + producibleTypes);
}
}
if (selectedMediaType != null) {
selectedMediaType = selectedMediaType.removeQualityValue();
for (HttpMessageConverter<?> converter : this.messageConverters) {
GenericHttpMessageConverter genericConverter = (converter instanceof GenericHttpMessageConverter ?
(GenericHttpMessageConverter<?>) converter : null);
if (genericConverter != null ?
((GenericHttpMessageConverter) converter).canWrite(targetType, valueType, selectedMediaType) :
converter.canWrite(valueType, selectedMediaType)) {
body = getAdvice().beforeBodyWrite(body, returnType, selectedMediaType,
(Class<? extends HttpMessageConverter<?>>) converter.getClass(),
inputMessage, outputMessage);
if (body != null) {
Object theBody = body;
LogFormatUtils.traceDebug(logger, traceOn ->
"Writing [" + LogFormatUtils.formatValue(theBody, !traceOn) + "]");
addContentDispositionHeader(inputMessage, outputMessage);
if (genericConverter != null) {
genericConverter.write(body, targetType, selectedMediaType, outputMessage);
} else {
((HttpMessageConverter) converter).write(body, selectedMediaType, outputMessage);
}
} else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Nothing to write: null body");
}
}
return;
}
}
}
if (body != null) {
Set<MediaType> producibleMediaTypes =
(Set<MediaType>) inputMessage.getServletRequest()
.getAttribute(HandlerMapping.PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE);
if (isContentTypePreset || !CollectionUtils.isEmpty(producibleMediaTypes)) {
throw new HttpMessageNotWritableException(
"No converter for [" + valueType + "] with preset Content-Type '" + contentType + "'");
}
throw new HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException(getSupportedMediaTypes(body.getClass()));
}
}
......
}
이렇게 스프링 컨트롤러를 호출해 메서드가 실행되는 과정을 코드 레벨에서 살펴보았습니다. 더 디테일 한 부분까지 하나하나 뜯어보고 싶었지만 시간이 부족해서(사실 부족하다는 핑계로…..) 모든 부분을 정리 못 한 게 아쉽습니다. 다 하고 보니 기왕 하는 거 조금만 더 꼼꼼하게 할 걸 하고 후회가 많이 되네요.. 여하튼 긴 글 읽어주셔서 감사합니다.
3. 정리
컨트롤러의 동작 원리에 대해 코드 레벨에서 하나씩 살펴보았습니다. 컨트롤러는 최초 사용자 요청을 받으면 DispatcherServlet이 onRefresh 메서드를 통해 필드를 초기화며, 이후 아래와 같은 과정을 거쳐 사용자 요청을 처리합니다. 내용이 복잡한 만큼 동작 과정을 직접 디버깅해보며 학습해 보실 것을 추천드립니다.
- doService
- diDispatch
- getHandler
- getHandlerAdapter
- handle
- invokeHandlerMethod